MATLAB、Python、Scilab、Julia比較ページはこちら
https://www.simulationroom999.com/blog/comparison-of-matlab-python-scilab/
はじめに
の、
MATLAB,Python,Scilab,Julia比較 第3章 その42【非極大値抑制⑦】
非極大値抑制をプログラムで実現してみる。
今回はPython(NumPy)で実施。
動作確認用処理【再掲】
まずは、非極大値抑制の実験の処理手順を再掲
- Sobelフィルタ等の微分フィルタで以下を推定
- x軸、y軸の濃淡変化量
- 変化強度(ノルム)
- 「x軸、y軸の濃淡変化量」から勾配方向角を推定
- arntan関数を利用
- 勾配方向を垂直(UD)、水平(LR)、斜め右上から右下(RULD)、斜め左上から右下の4パターンに丸め。
- 勾配方向角に応じて極大値評価をして非極大値だったら「変化強度(ノルム)」 を0値埋め
- 画像出力
これをPython(NumPy)で実現する。
Pythonコード
Pythonコードは以下になる。
import numpy as np
import cv2
# 畳み込み演算
def convolution2d(img, kernel):
m, n = kernel.shape # カーネルサイズ取得
# カーネル中心からみた幅
dy = int((m-1)/2) # カーネル上下幅
dx = int((n-1)/2) # カーネル左右幅
h, w = img.shape # イメージサイズ
out = np.zeros((h, w)) # 出力用イメージ
# 畳み込み
for y in range(dy, h - dy):
for x in range(dx, w - dx):
out[y][x] = np.sum(img[y-dy:y+dy+1, x-dx:x+dx+1]*kernel)
return out
# Non maximum Suppression
def non_maximum_suppression(G, theta):
h, w = G.shape
out = G.copy()
# 勾配方向を4方向(LR,UD,RULD,LURD)に近似
theta[np.where(( -22.5 <= theta) & (theta < 22.5))] = 0 # LR ─
theta[np.where(( 22.5 <= theta) & (theta < 67.5))] = 45 # RULD /
theta[np.where(( 67.5 <= theta) & (theta < 112.5))] = 90 # UD │
theta[np.where(( 112.5 <= theta) & (theta < 157.5))] = 135 # LURD \
theta[np.where(( 157.5 <= theta) & (theta < 180.0))] = 0 # LR ─
theta[np.where((-180.0 <= theta) & (theta < -157.5))] = 0 # LR ─
theta[np.where((-157.5 <= theta) & (theta < -112.5))] = 45 # RULD /
theta[np.where((-112.5 <= theta) & (theta < -67.5))] = 90 # UD │
theta[np.where(( -67.5 <= theta) & (theta < -22.5))] = 135 # LURD \
# 現画素の勾配方向に接する2つの画素値を比較し、現画素が極大値でなければ0にする。
for y in range(1, h - 1):
for x in range(1, w - 1):
if theta[y][x] == 0: # LR ─
if (G[y][x] < G[y][x+1]) or (G[y][x] < G[y][x-1]):
out[y][x] = 0
elif theta[y][x] == 45: # RULD /
if (G[y][x] < G[y-1][x+1]) or (G[y][x] < G[y+1][x-1]):
out[y][x] = 0
elif theta[y][x] == 90: # UD │
if (G[y][x] < G[y+1][x]) or (G[y][x] < G[y-1][x]):
out[y][x] = 0
else: # LURD \
if (G[y][x] < G[y+1][x+1]) or (G[y][x] < G[y-1][x-1]):
out[y][x] = 0
return out
def non_maximum_suppression_test():
# 入力画像の読み込み
img = cv2.imread("dog.jpg")
b = img[:,:,0]
g = img[:,:,1]
r = img[:,:,2]
# ガウシアンフィルタ用のkernel
kernel_gauss = np.array([[1/16, 2/16, 1/16],
[2/16, 4/16, 2/16],
[1/16, 2/16, 1/16]])
# Sobelフィルタ用のKernel
kernel_sx = np.array([[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]])
kernel_sy = kernel_sx.T
# SDTVグレースケール
gray_sdtv = np.array(0.2990 * r + 0.5870 * g + 0.1140 * b, dtype='uint8')
# ガウシアンフィルタ
img_g = convolution2d(gray_sdtv, kernel_gauss)
# Sobelフィルタ
Gx = convolution2d(img_g, kernel_sx)
Gy = convolution2d(img_g, kernel_sy)
# 勾配強度と角度
G = np.sqrt(Gx**2 + Gy**2)
theta = np.arctan2(Gy, Gx) * 180 / np.pi
cv2.imwrite("dog_nms_G.jpg",np.abs(G)) # 255オーバーあり
cv2.imwrite("dog_nms_theta.jpg",np.abs(theta)) # -180~180
# 極大値以外を除去(Non maximum Suppression)
G_nms = non_maximum_suppression(G, theta)
cv2.imwrite("dog_nms.jpg",G_nms) # 255オーバーあり
return
non_maximum_suppression_test()処理結果
そして処理結果。
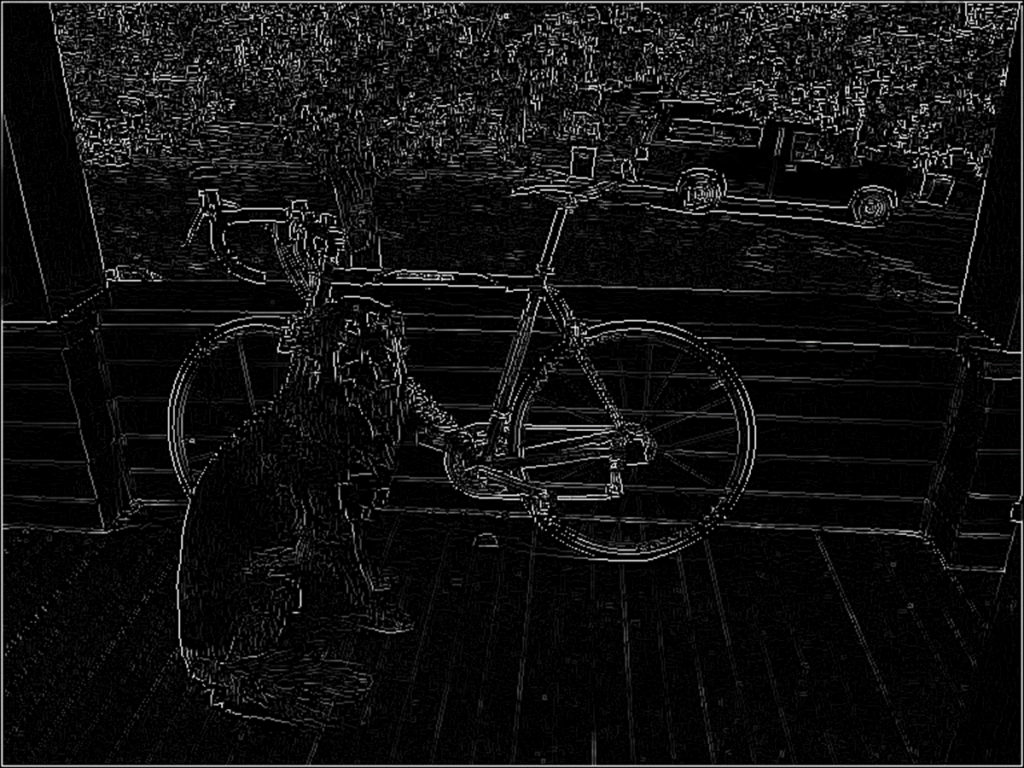

考察
これもMATLABと同じ結果が得られた。
(演算が一緒だから当たり前ではあるが・・・。
気になる点と言えばコード上のこれ。
theta[np.where(( -22.5 <= theta) & (theta < 22.5))] = 0線形インデックスサーチになる。
MATLABでやったときは論理インデックスサーチを使用していたが、
今回はあえて線形インデックスサーチにしてみた。
ちなみに、論理インデックスサーチ、線形インデックスサーチは
MATLAB,Python(NumPy)ともに実施可能。
まとめ
- Python(NumPy)で非極大値抑制を実施。
- MATLABと同一の結果が得られた。
- MATLABでは論理インデックスサーチを使用したが、ここではあえて線形インデックスサーチを使用。
MATLAB、Python、Scilab、Julia比較ページはこちら




コメント